5 MIN READ
Identification of Early Season Insects in Corn
March 3, 2024
Table 1. Timing of plant injuries from early season corn pests.
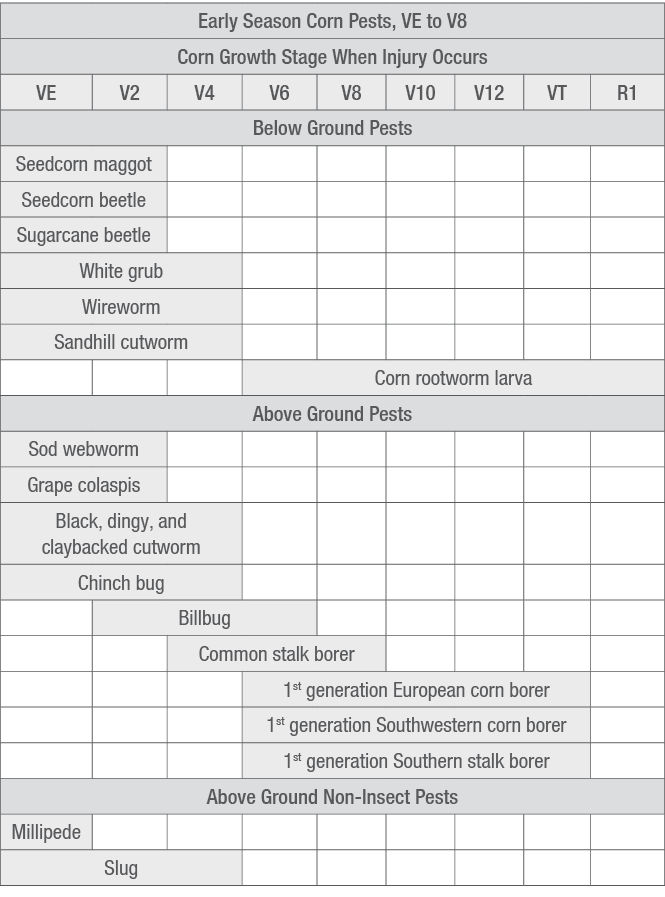
Table 2. Diagnostic Injury of Common Early Season Corn Pests.
Where to Find Insect Pests
Early season insects can be found attacking the seed (seedcorn maggot, seedcorn beetle), the seed and below-ground parts of the seedling (wireworm, sugarcane beetle), the roots (white grubs), or the underground stem (sandhill cutworm). A small garden trowel or pocketknife are handy tools to use when searching for below-ground pests.
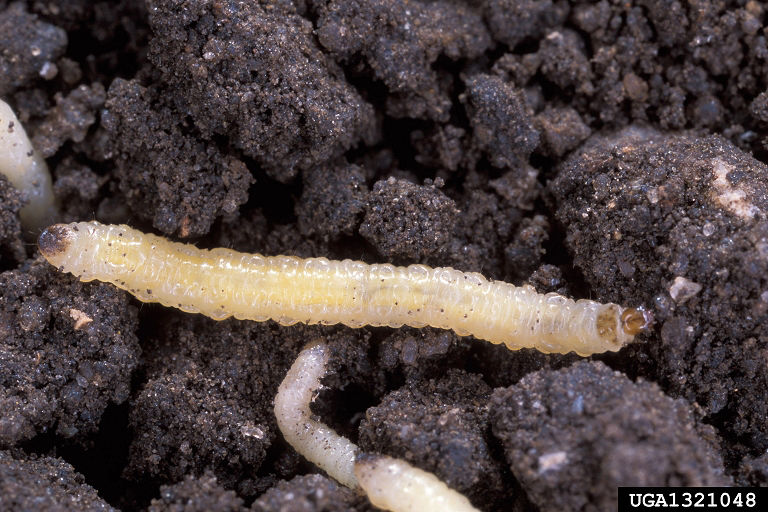
Two examples of below-ground pests that might be found while digging are corn rootworm larvae and white grubs. Corn rootworm larvae may be present during the later stages of early season growth, but may be too small to readily detect. If detected, they will have a brown to black head and a brown to black anal plate (Figure 4, Table 2). White grubs—a generic term for the larval stage of insects like the Japanese beetle, rose or sand chafer, and May or June beetles, though true white grubs are the larval stage of May and June beetles—can be identified by the raster pattern, or the setae (hair) pattern on the posterior end (Figure 13, Table 2). Michigan State University has developed an excellent publication that can be used to help identify white grubs in the field: https://www.canr.msu.edu/news/severe-grub-damage-spotted-in-northern-michigan-grass-hay-field
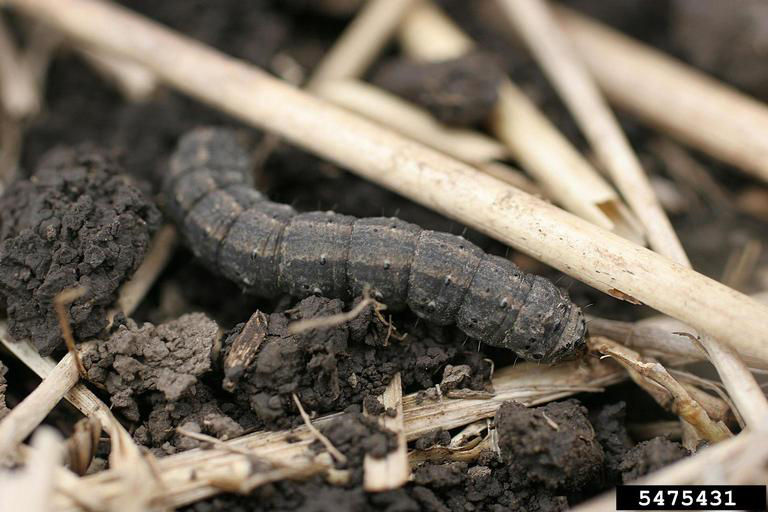
Some of these insect pests feed above ground but can also be found below ground. For example, the cutworm species feed above ground at night but spend the day under soil clods.
Reference Images
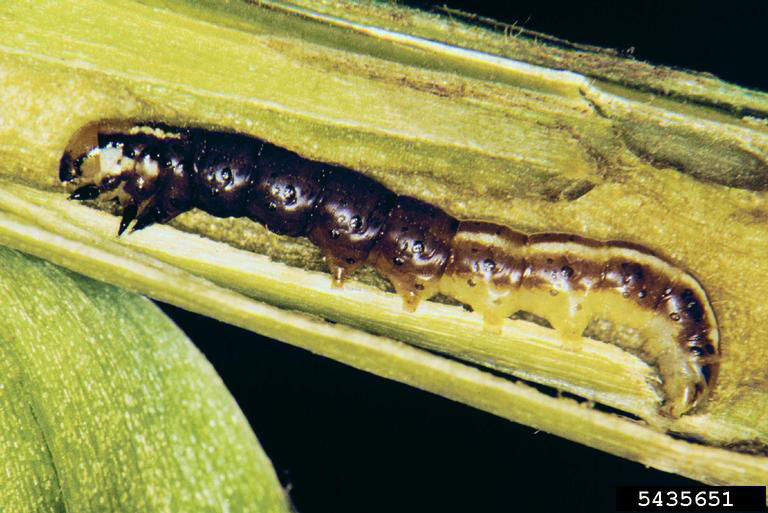
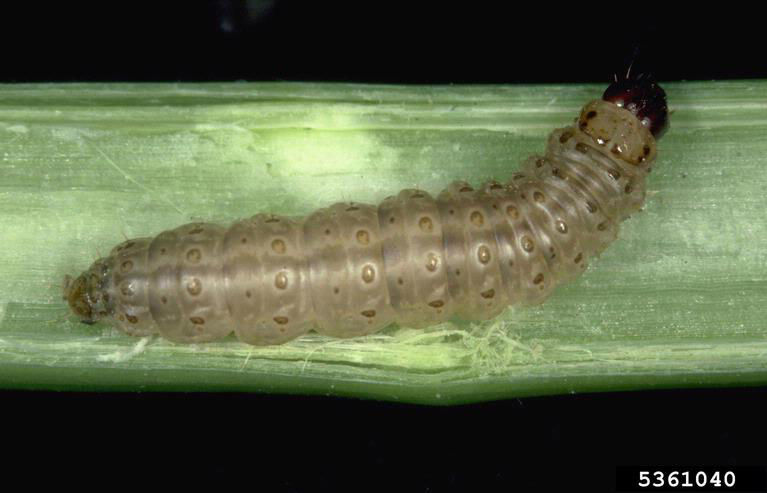
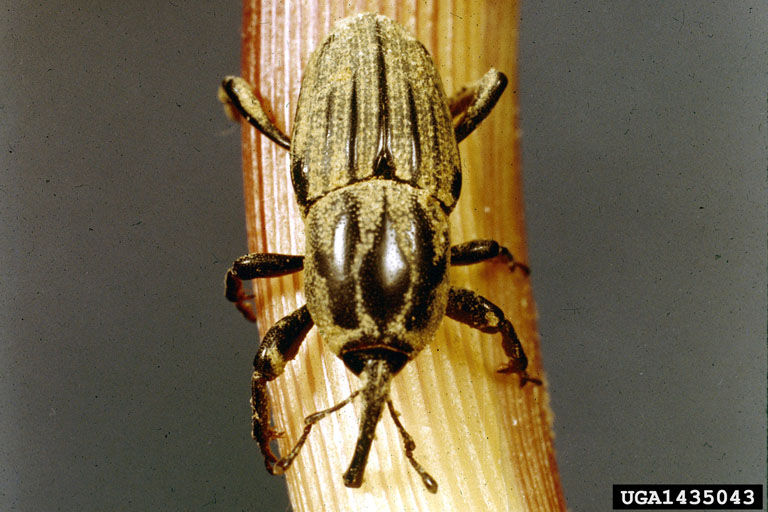
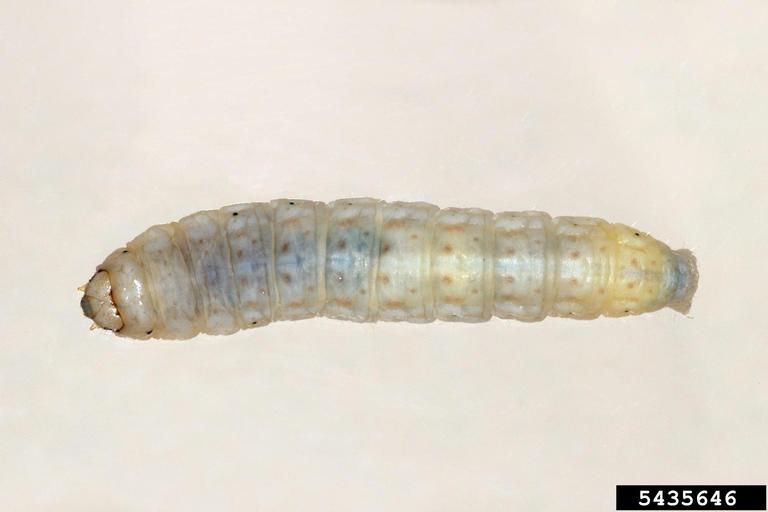
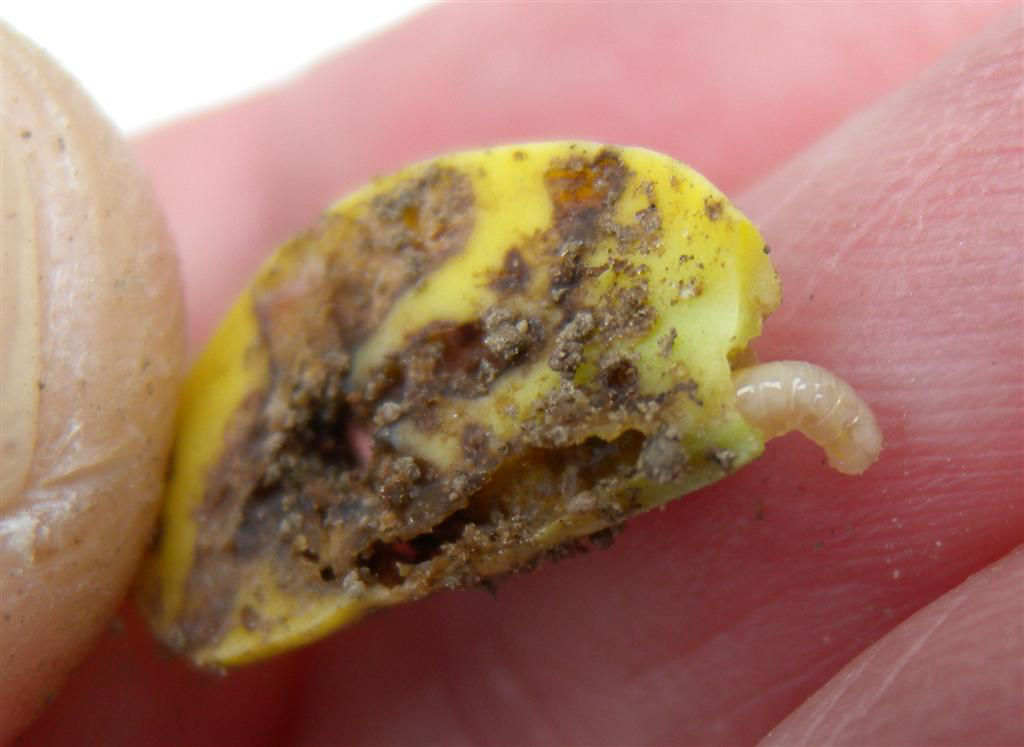
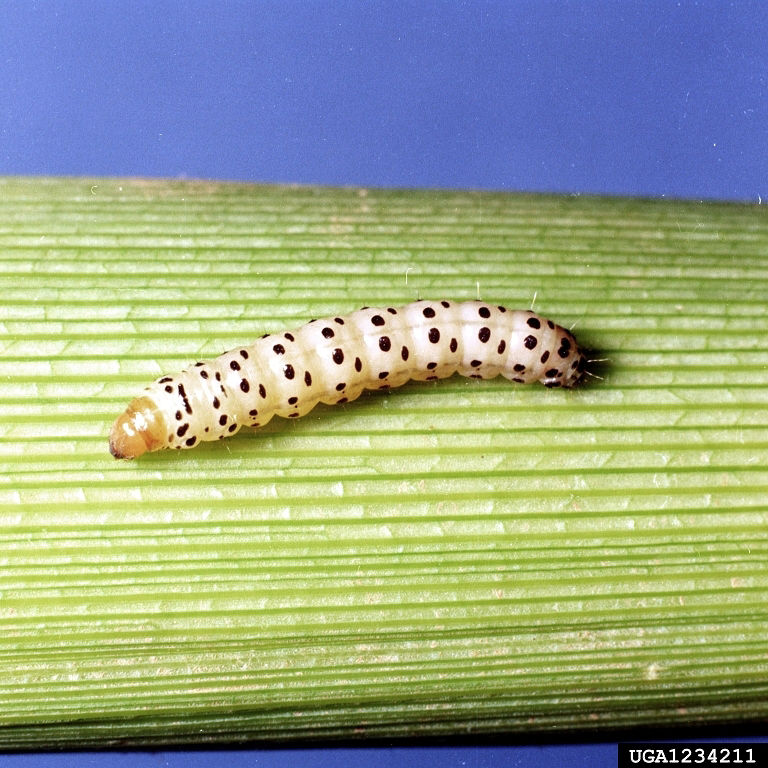
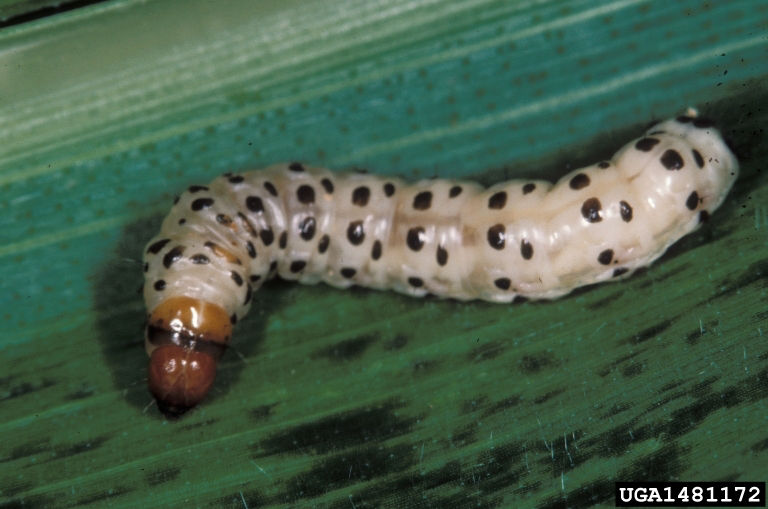
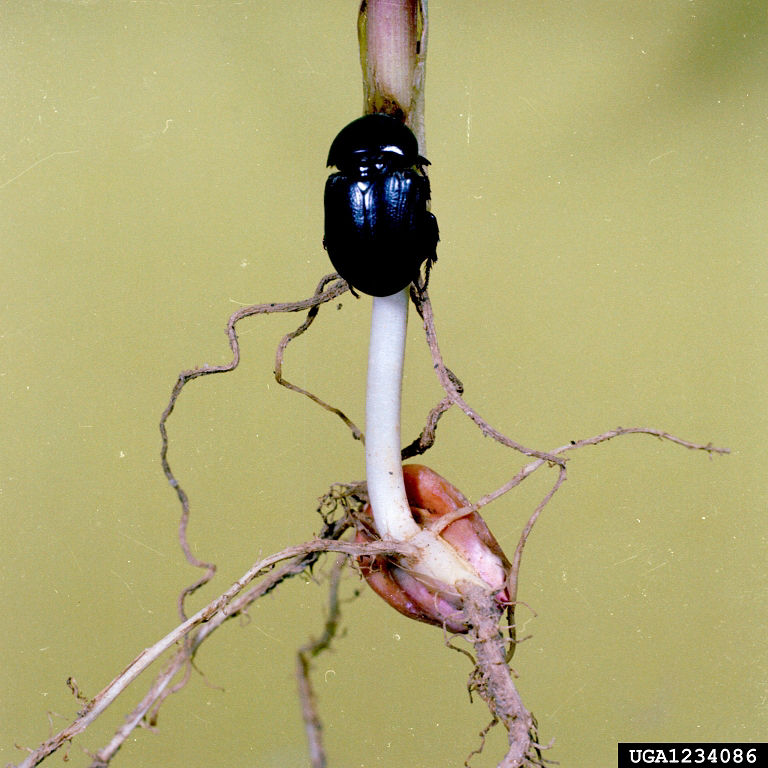
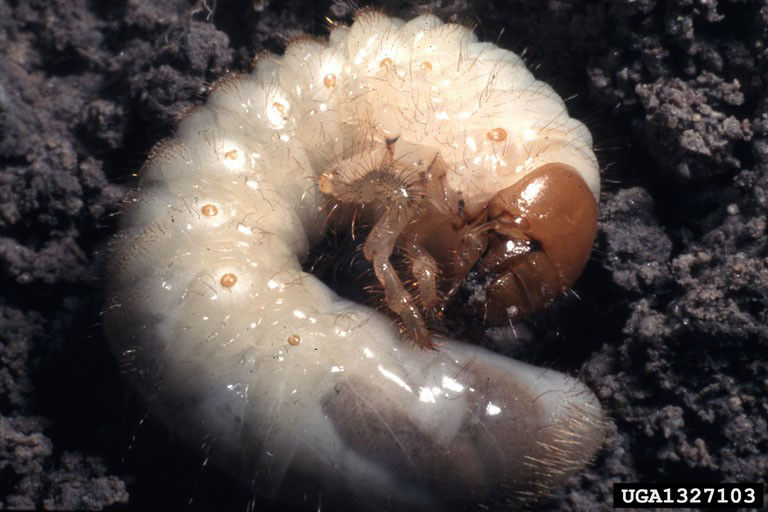













1215_66281
Disclaimer
Always read and follow pesticide label directions, insect resistance management requirements (where applicable), and grain marketing and all other stewardship practices.