7 MIN READ
Understanding Herbicide Adjuvants
November 1, 2022
The Function of Adjuvants
Adjuvants in herbicide formulations and spray mixtures can help improve herbicide application and performance. Herbicide labels, which MUST be read and followed, are the most important source of information for adjuvant recommendations and cover diverse use situations and tank mixtures. Adjuvant recommendations are specific for each herbicide product as researched and developed by the herbicide manufacturers. Adjuvants include spreaders, stickers, wetting agents, penetrants, stabilizing agents, compatibility agents, buffering agents, antifoam agents, and others.1
Adjuvants can be classified as activators and utility modifiers (or special purpose adjuvants):
- Activators, such as surfactants, crop oil concentrates (COC), and nitrogen (N) are normally used to help improve the performance of herbicides by increasing herbicide retention or penetration into leaf surfaces, improving rain fastness, or to decrease photodegradation of herbicides.2
- Utility modifiers, such as buffering, antifoam, and drift control agents, typically modify the characteristics of the spray solution and product compatibility.
Labels MUST be followed since use of an herbicide product in a manner inconsistent with its labeling is a violation of federal law. Each herbicide product has adjuvant requirements that are specified on the herbicide label. The label provides guidance and adjuvant options to address tank mixtures, environmental conditions, or weed species characteristics. Some herbicides, such as Roundup PowerMAX® 3 Herbicide, are formulated with sufficient adjuvants and may not require the use of additional adjuvants. Other herbicides have specific adjuvant recommendations that MUST be added to the spray mixture. Each herbicide manufacturer may have supplemental labels or fact sheets that provide additional guidance for the use of adjuvants for specific application situations, weed species, crops, or tank mixtures.
There is a diverse array of adjuvant products and brands. Therefore, the applicator must understand the composition and function of each product while considering expected environmental conditions at the time of application to properly match the adjuvant to individual herbicides or tank mixtures.
Types of Adjuvants
Adjuvants that can be used with herbicides include surfactants, oil concentrates, nitrogen fertilizers, spreader-stickers, wetting agents, and penetrants.1,2,3
- Non-ionic surfactants (NIS) are dispersing agents to help improve plant coverage and penetration of foliar-applied herbicides with low crop toxicity.
- Crop oil concentrates (COC) are derived from petroleum.
- Methylated seed oils (MSO) function like other oil concentrates but are derived from seed oils.2
- High surfactant oil concentrates (HSOC) are emulsifiable oil-based products containing 25 to 50% surfactant (wt/wt) in a minimum of 50% oil (wt/wt) which can be MSO or COC based.
- Nitrogen fertilizer products, used at recommended rates, can act as adjuvants to help improve the performance of certain herbicides, especially under hard water conditions, drought, or in tank mixtures. Spray-grade ammonium sulfate (AMS) or urea ammonium nitrate (UAN) are common nitrogen fertilizer adjuvants. Nitrogen fertilizer solutions are generally recommended in conjunction with NIS or COC.
- Blended adjuvants contain specific combinations of special purpose and/or activator adjuvants that serve multiple functions.2
- The risk for crop injury may be increased with COC, MSO, and HSOC products compared to surfactants.3
Table 1. Adjuvant recommendations for Bayer herbicides.*
(Individual herbicide labels MUST be read and followed. The information in this table does not replace the label)
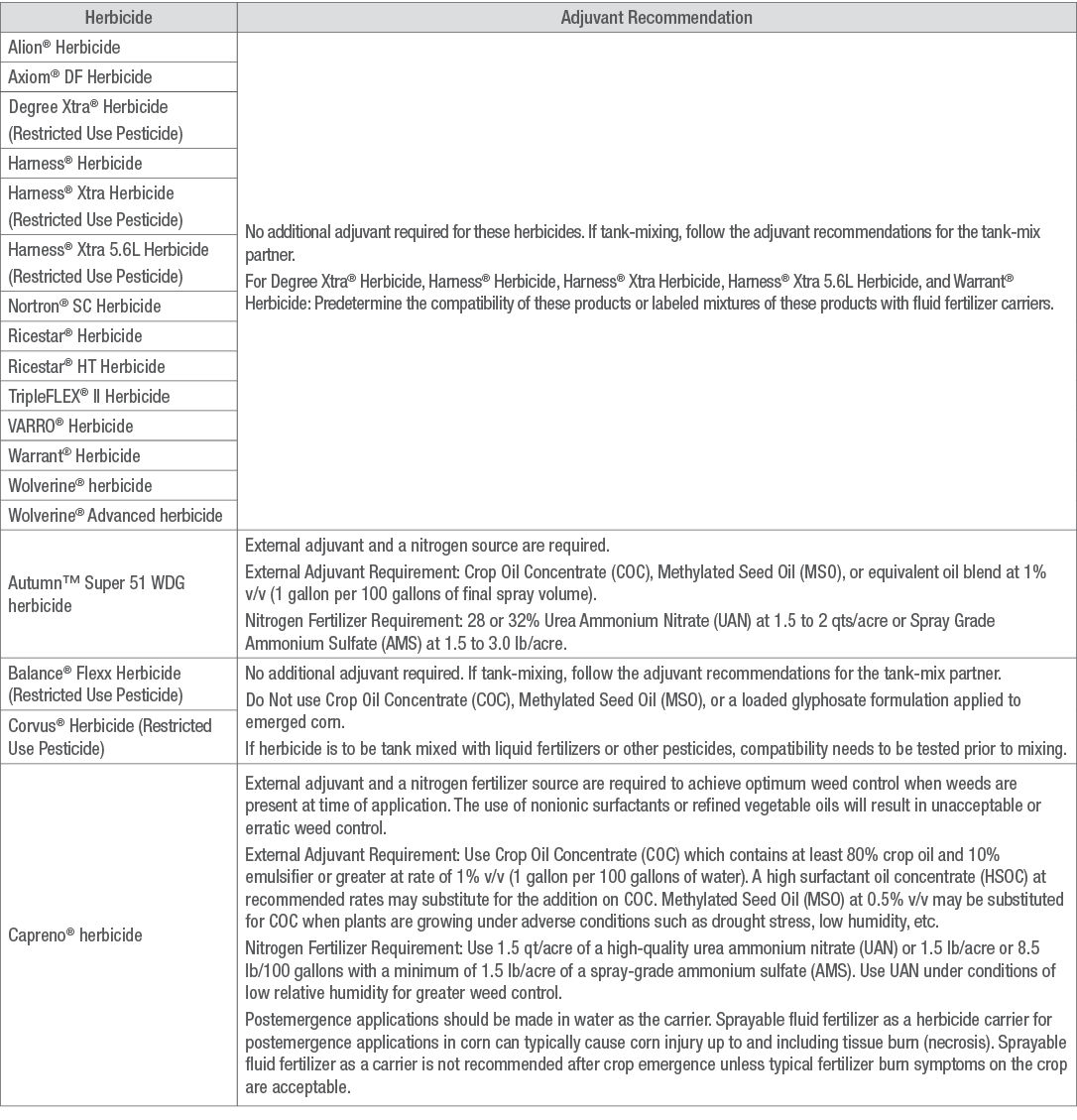
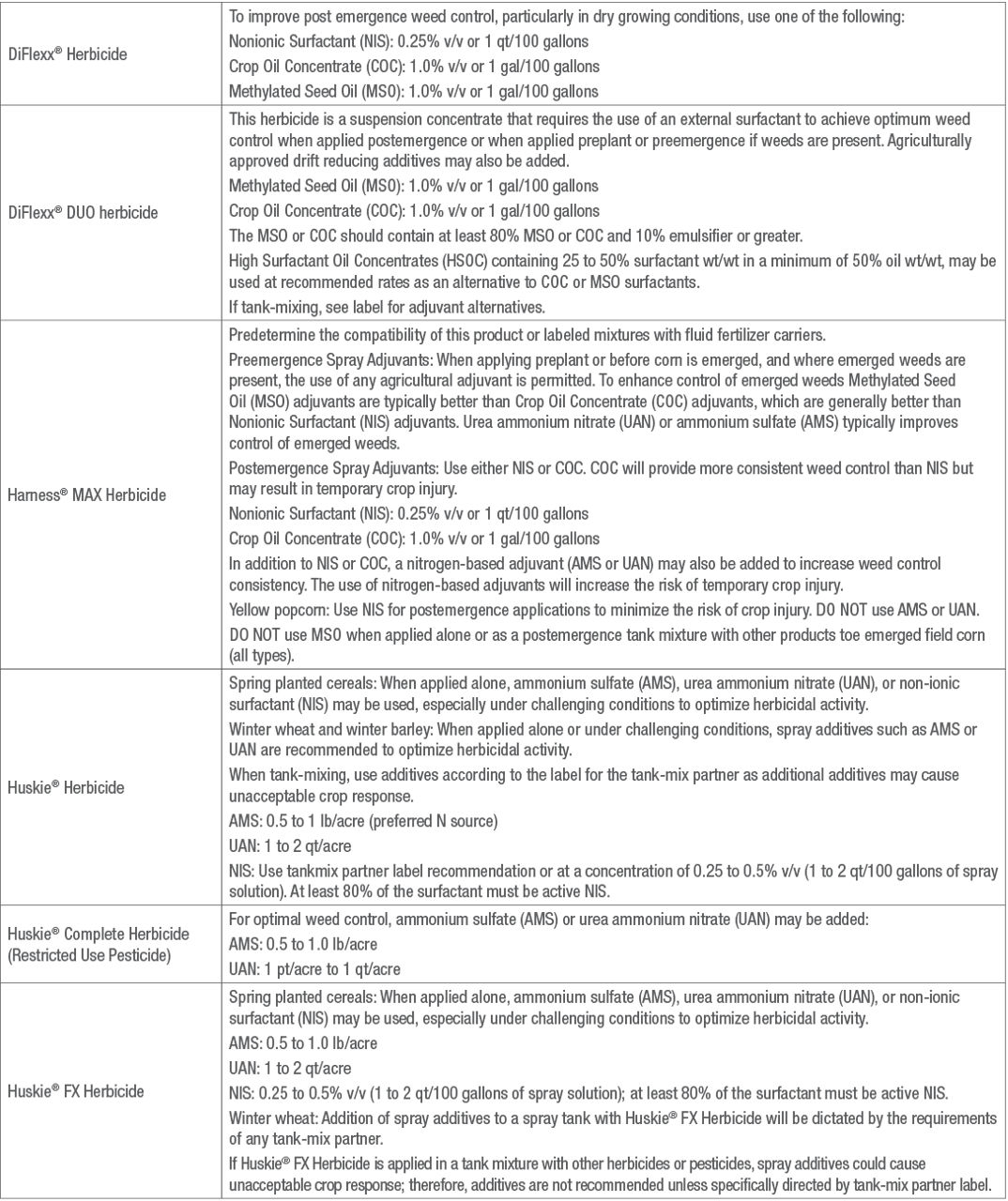
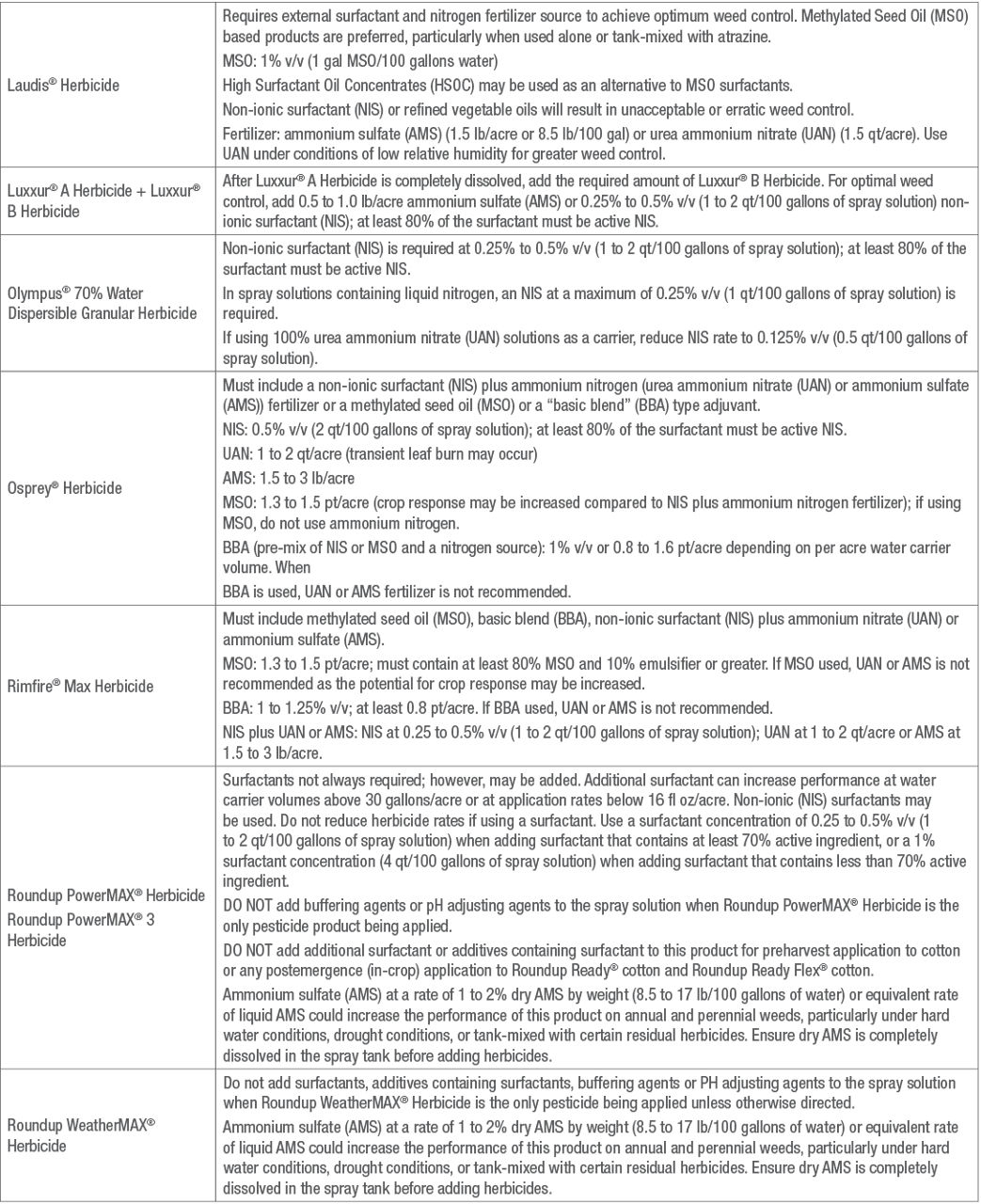
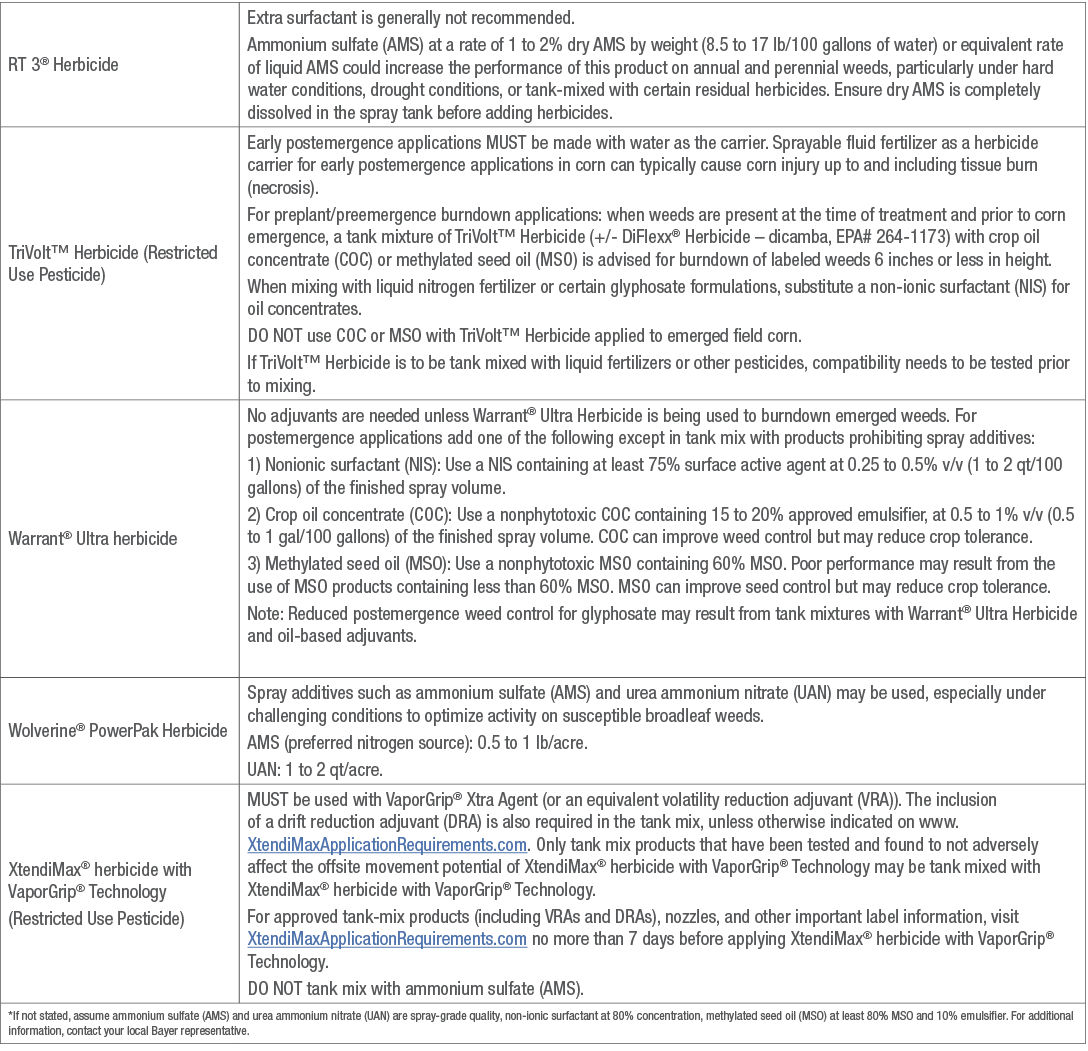
Sources:
1Jordan, T., Johnson, B., and Nice, G. 2011. Adjuvants used with herbicides: Factors to consider. Pest & Crop. Issue 25. Purdue University. https://extension.entm.purdue.edu/pestcrop/2011/issue25/index.html#adjuvant/.
2Curran, W.S. and Lingenfelter, D.D. 2009. Adjuvants for enhancing herbicide performance. Agronomy Facts 37. Penn State Extension. https://extension.psu.edu/adjuvants-for-enhancing-herbicide-performance/.
3Swoboda, R. (Hartzler, R., Iowa State University) 2013. Relearning to accept herbicide injury to crops. WallacesFarmer. https://www.farmprogress.com/story-relearning-accept-herbicide-injury-crops-9-95965/.
Hartzler, B. 2001. Role of spray adjuvants with postemergence herbicides. Integrated Crop Management. Iowa State University. https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/role-spray-adjuvants-postemergence-herbicides/.
1026_48301
Disclaimer
Always read and follow pesticide label directions, insect resistance management requirements (where applicable), and grain marketing and all other stewardship practices.