Understanding Pesticide Labels
January 14, 2025
- Pesticide labels are legal documents containing directions for use, handling, storage, and disposal of a pesticide product.
- With so many sections on a label, it can be difficult to discern what you need to know.
- This document can help you understand how a label is organized and what information is provided within each section.
Pesticide labels are legal documents that are required to provide directions on how to properly mix, apply, store, and dispose of a pesticide product. These directions are designed to help ensure the safe and effective use of pesticides. Failure to comply with label directions can potentially harm humans and the environment, as well as lead to possible legal liability. The label must be read and understood prior to use.1
The number on the text below matches the number in the box for each section of the label.
1 – Use Classification Statement:
- Pesticides are classified as either a General Use Pesticide (GUP) or Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP).2
- Pesticides labeled as a Restricted Use Pesticide (RUP) can only be applied by a certified applicator or someone under the certified applicator’s direct supervision.3
2 – Brand or Trade Name of the Product:
- The product name usually does not identify all of the active ingredients in a pesticide product.
- There may be several trade names for one common name due to different formulations or manufacturers.
3 – Type of Pesticide:
- Most labels will state the type of pesticide by indicating, for example, if it is an insecticide or herbicide.
4 – EPA Registration Number and Establishment Number:
- This section indicates that the pesticide product has been registered and its label was approved for sale by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). It also identifies the facility that produced the product.
5 – Active Ingredient:
- Every label must list all of the active ingredients in a product by weight and/or pounds per gallon for each active ingredient.
- The common and chemical names are unique identifiers of each pesticide active ingredient.
- Inert ingredients—sometimes referred to as “other ingredients”—such as emulsifiers or solvents, must be included in the label and are usually expressed as a total percentage of weight, but are not required to be listed by name.
- The net contents of the container along with the name and address of the manufacturer must be included.
6 – Precautionary Statements:
- 6a – Hazards to human or animals
- 6b – Environmental hazards
- Directions for users to protect their safety and the safety of the environment.
7 – Signal Words:
- Helps users assess the toxicity of each product. The signal word is based on the toxicity of all of the contents of a formulated product.
- Danger-Poison, with skull and crossbones symbol – product is highly toxic by any route of entry into the body.
- Danger – product is corrosive and can cause irreversible skin or eye irritation.
- Warning – product is moderately toxic if exposure is by mouth, skin, or inhalation.
- Caution – product is slightly toxic if exposure is by mouth, skin, or inhalation; or will cause a slight skin or eye irritation.4
8 – Statement of Practical Treatment (also called First Aid Statement):
- Tells users and medical professionals the type of emergency first aid needed in case of an accident.
9 – Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Specific information outlining the minimum protective clothing and gear that must be worn during handling, mixing, and application of the product.
SPECIMAN LABEL FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY

10 – Directions for Use:
Pesticide labels will typically have various subsections pertaining to specific directions including some, or all, of the following:
- Proper mixing, handling, and application procedures.
- Pests controlled
- Crops approved for use
- Application use rates
- Application methods and timing
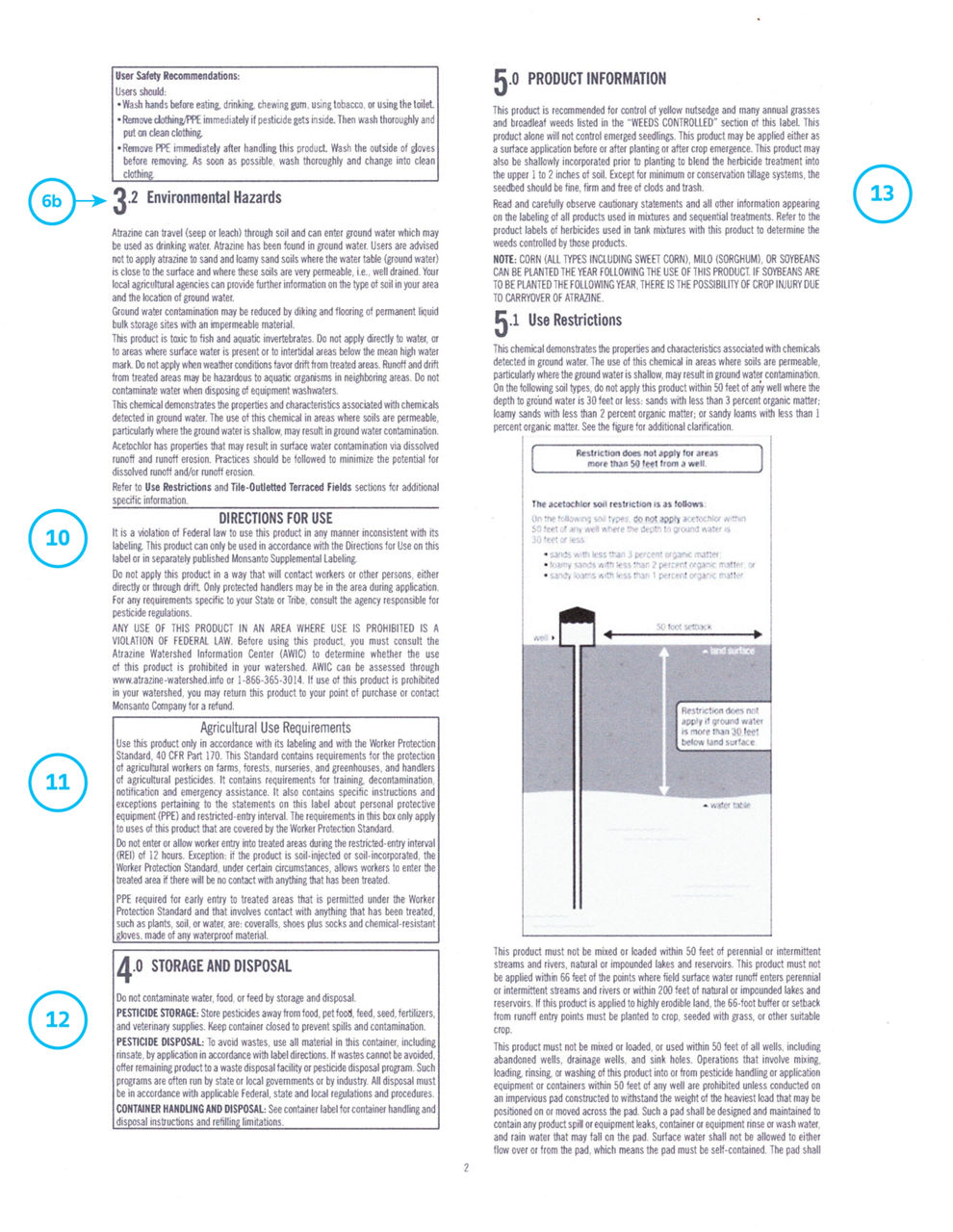
- Ground and surface water protection requirements
- Application equipment and calibration
- Product mixing with other pesticides and adjuvants in water, fertilizer, or irrigation water.
- Drift management, resistance management, and other pesticide-specific information.
- Pre-harvest Intervals (PHI)
11 – Agricultural Use Requirements:
- This information is outlined by a box in the label.
- Worker Protection Standard (WPS) requirements will be listed, outlining specific safety measures for agricultural workers and pesticide handlers.
- Restricted Entry Intervals (REI) indicates how much time must pass after an application of the pesticide before workers are allowed into the treated area.
12 – Storage and Disposal:
- Guidelines for properly storing the product, the cleaning and disposal of containers, and handling spills.
13 – Product Information:
- Indicates the pest that the product controls or suppresses.
- May also include any use restrictions for the pesticide.
Attention:
This specimen label is provided for general information only.
- This pesticide product may not be available or approved for sale or use in your area.
- It is your responsibility to follow all federal, state, and local laws and regulations regarding the use of pesticides.
- Before using any pesticide, be sure the intended use is approved in your state or locality.
- Your state or locality may require additional precautions and instructions for use of this product that are not included here.
- Bayer does not guarantee the completeness or accuracy of this specimen label. The information found in this label may differ from the information found on other product labels. You must have the EPA approved labeling with you at the time of use and must read and follow all label directions.
- You should not base any use of a similar product on the precautions, instructions for use, or other information you find here.
- Always follow the precautions and instructions for use on the label of the pesticide you are using.
Sources
1Pesticide Environmental Stewardship. How to read the label. https://pesticidestewardship.org/homeowner/how-to-read-the-label/
2Puckett, G.J., Hygnstrom, J.R., Bauer, E.C., and Weisbrod, J.M. 2021. Understanding the pesticide label. University of Nebraska Extension. NebGuide G1955. https://extensionpubs.unl.edu/publication/g1955/2021/pdf/view/g1955-2021.pdf
3United States Environmental Protection Agency. 2024. Restricted use products (RUP) report. https://www.epa.gov/pesticide-worker-safety/restricted-use-products-rup-report
4Gripp, S. 2024. What you need to know about reading a pesticide label. Pennsylvania State University Extension. https://extension.psu.edu/what-you-need-to-know-about-reading-a-pesticide-label
Web sources verified 01/03/25. 1026_48516
Disclaimer
Always read and follow pesticide label directions, insect resistance management requirements (where applicable), and grain marketing and all other stewardship practices.