How can Variable Rate Irrigation Improve Crop Production?
November 21, 2023
Irrigation Overview:
- Crop water use is influenced by local atmospheric conditions, soil type, crop growth stage, planting date and planting density.
- Substantial reductions in yield potential can occur if the plant does not receive enough water to meet evapotranspiration demands during peak water use in the reproductive growth stages.
- Irrigation management usually schedules an application of water before the crop reaches a state of severe water stress.
- Normal irrigation systems simply apply the same amount of water to the entire field regardless of soil type.
- Variable rate irrigation (VRI) technologies can automatically model and create water application prescriptions for different soil or crop types, and then send those recommendations directly to a VRI system.
Variable Rate Irrigation systems are based on mapping programs such as Climate FieldView™ that can help determine where irrigation may be needed in fields based on soil types, historical yields, fertility, and other factors (Figure 1).
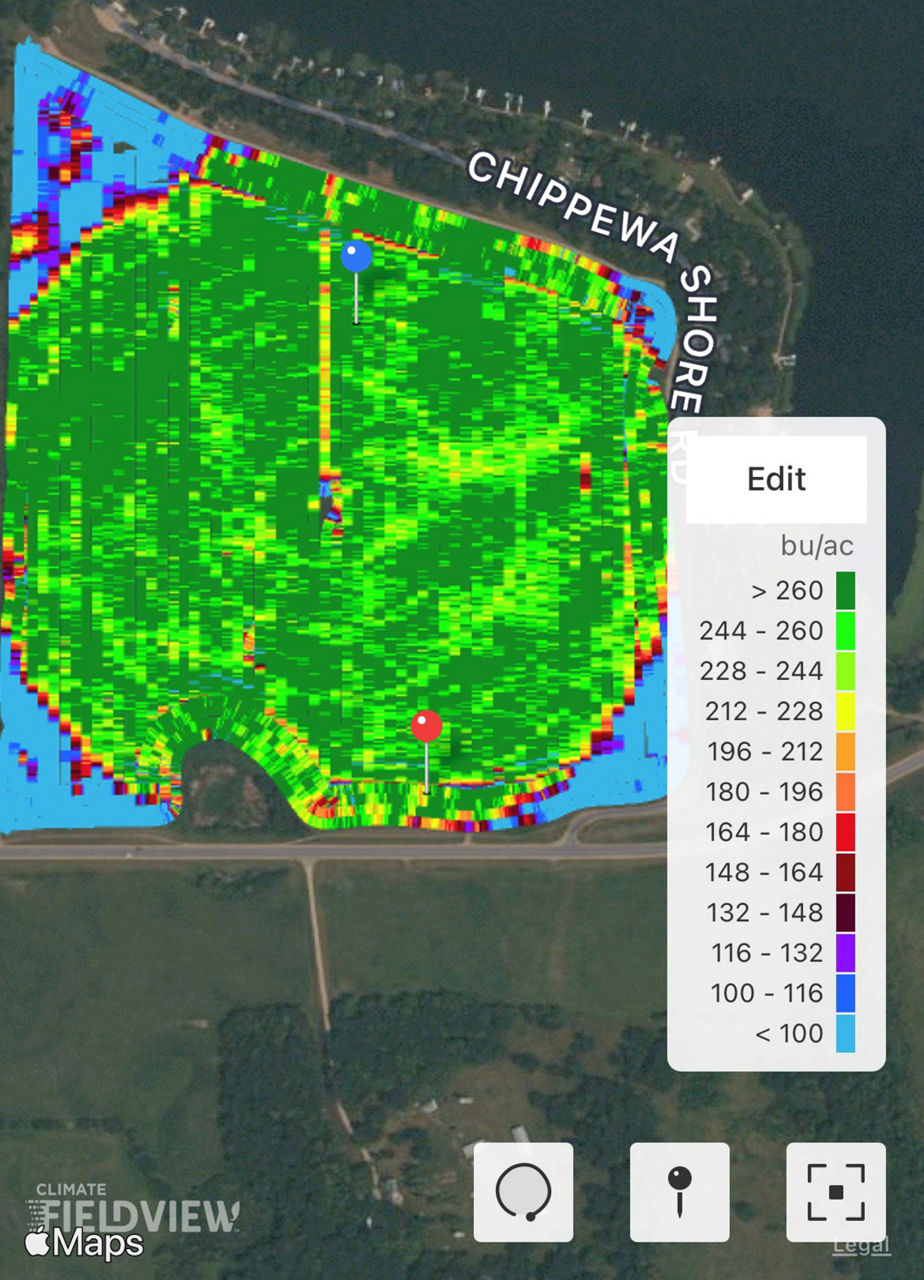
Irrigation manufacturer, Lindsay Corporation, offers a program called Zimmatic Precision VRI™. Variable Rate Irrigation provides varying irrigation levels across the pivot to help ensure the precise delivery of water to crops throughout their lifecycle. Essentially, it helps apply the right amount of water or chemicals to the right places at the right time.1
Benefits for using Variable Rate Irrigation (Lindsay™ manufacturing):
- Increased efficiency and profitability potential by helping to prevent overwatering and underwatering. In other words, getting the water to the areas where it can be used the most, or limiting the water in areas where it is not needed.
- Maximizing yield potential by helping to provide the right amount of water at the optimum timings during the season as well as preparing the fields for next season. Soil and yield map data is the basis that drives VRI.
- Save water by turning off sections that don’t need it, and then utilizing the saved water for the areas of the field that need extra water. VRI use in the future can help to limit total water use in a climate where water use is being critically scrutinized and limited.2
- Minimize nutrient leaching and runoff by matching water rates to soil type and topography, thus helping to prevent oversaturation in problem areas of the field.
- Greater control by taking the guesswork out of running an irrigation system with a flat rate regardless of the soil type or topography using field maps and water rate prescriptions.
- Nozzle changing is not needed with a constant system flow rate as VRI can control the flow rate without hardware changes. This helps reduce or eliminate the downtime used for renozzling.
- Optimize chemical use by tailoring chemigation and fertigation with a solution like VRI technology to apply exactly the right amount of water AND chemicals to specific areas of the field.
Irrigated land has the potential to produce higher yielding crops when compared to dryland. Irrigated agriculture accounts for 20% of the total cultivated land and contributes 40% of the total food produced worldwide.3 Irrigation can help increase yield potential, help enhance farm profit, and if correctly done, helps with soil structure.4
Ultimately, VRI is a great tool that can help improve profitability while saving resources. The combination of enhanced genetics, that perform well under irrigation, and a fine-tuned irrigation system should be a consideration for the future.
For additional irrigation information, please see Corn Irrigation Timing and Water Use Efficiency.
Channel Agronomist
Derek Crompton
Sources:
1How variable rate irrigation (VRI) can make a difference. 2022. Lindsay Corporation. https://www.lindsay.com/usca/en/resource/how-variable-rate-irrigation-can-make-a-difference/
2Becker, T. and Sharma, V. 2022. Can variable rate irrigation combat groundwater issues in Minnesota? Minnesota Crop News. University of Minnesota Extension. https://blog-crop-news.extension.umn.edu/2022/03/can-variable-rate-irrigation-combat.html
3Water in agriculture. The World Bank. 2022. World Bank Group Water Global Practice. https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/water-in-agriculture
4The importance of variable rate irrigation in precision ag. GeoPard Agriculture. https://geopard.tech/blog/some-important-facts-about-variable-rate-irrigation/
Web sites verified 10/17/23 1110_307454
Disclaimer
Always read and follow pesticide label directions, insect resistance management requirements (where applicable), and grain marketing and all other stewardship practices.