10 MIN READ
Tar Spot Fungicide Timing Trial
March 24, 2022
TRIAL OBJECTIVE
Tar spot has been confirmed across a widespread area of the U.S. with reports of the disease in southern Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, New York, northwest Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin.
Cool, humid conditions with extended periods of leaf wetness promote tar spot development.
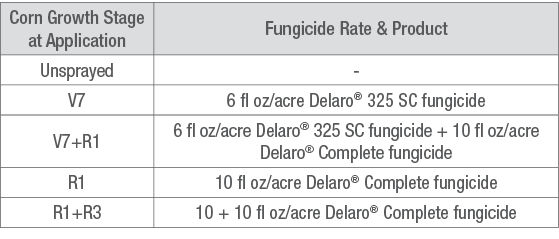
This trial evaluated control of tar spot with different application timings of Delaro® 325 SC fungicide and Delaro® Complete fungicide.
It is recommended to include fungicide applications with multiple modes of action to help mitigate yield loss from tar spot infection. Evaluation of these timings can help identify best management practices for control of tar spot.
RESEARCH SITE DETAILS
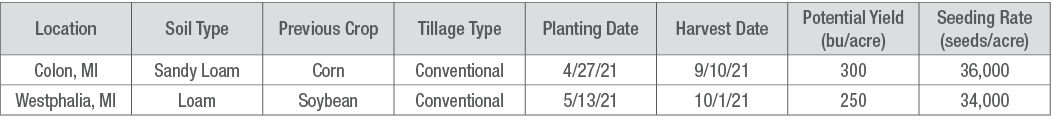
Two trial locations in Michigan (Colon and Westphalia) were selected as areas that had a history of above average tar spot pressure.
Treatments consisted of two DEKALB® brand corn products DKC49-72RIB Brand Blend and DKC52-34RIB Brand Blend of differing tar spot susceptibility (susceptible and less susceptible, respectively).
Two products (Delaro® 325 SC fungicide and Delaro® Complete fungicide) with four different application timings (V5, R1, V5+R1, and R1+R3 corn growth stages) were used along with an untreated plot.
Applications were made using a high clearance sprayer with 20 gallons/acre of water as carrier.
Colon was an irrigated location, and Westphalia was a rainfed location. Moisture load and frequency may have affected tar spot pressure.
UNDERSTANDING THE RESULTS
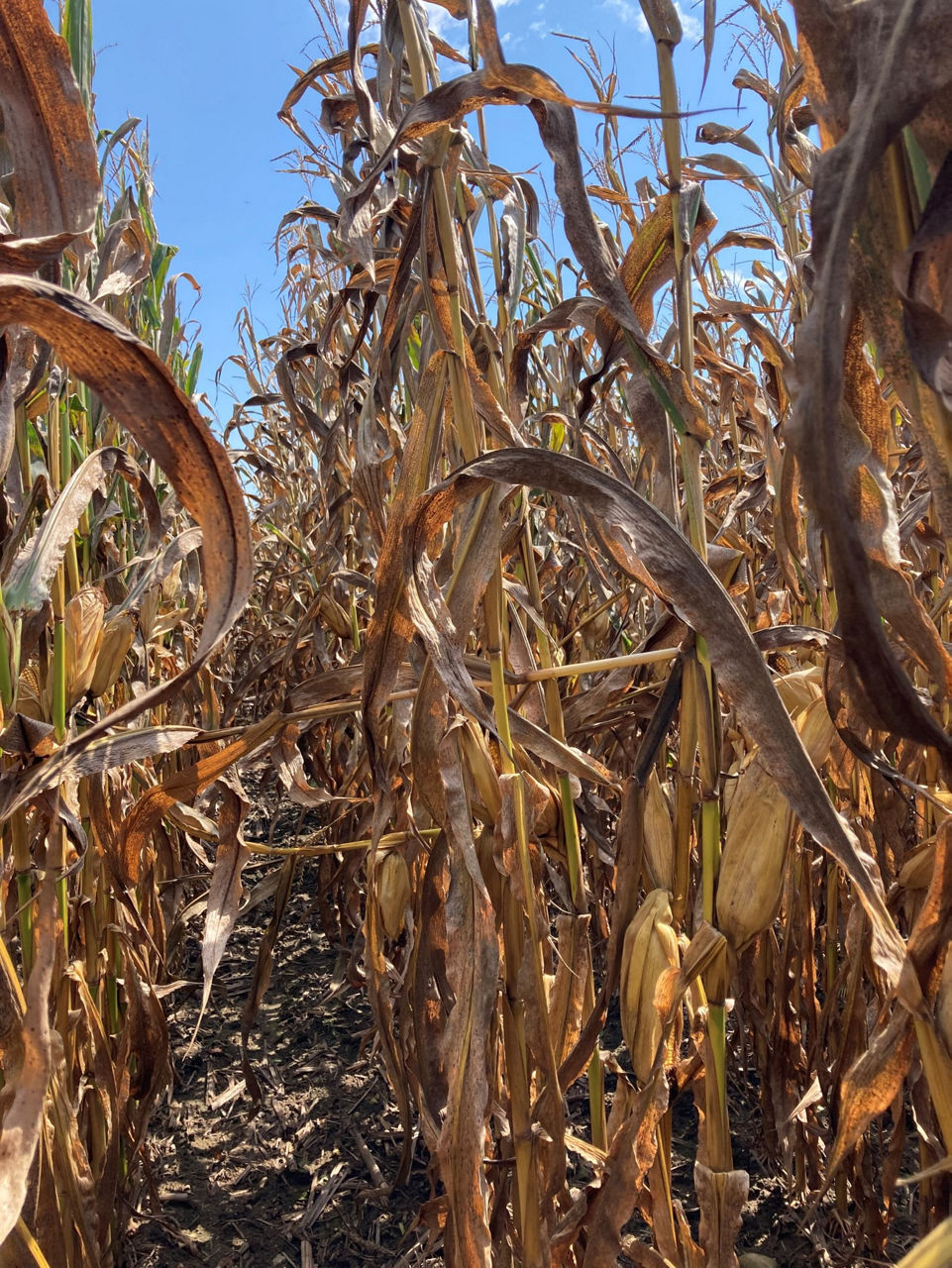
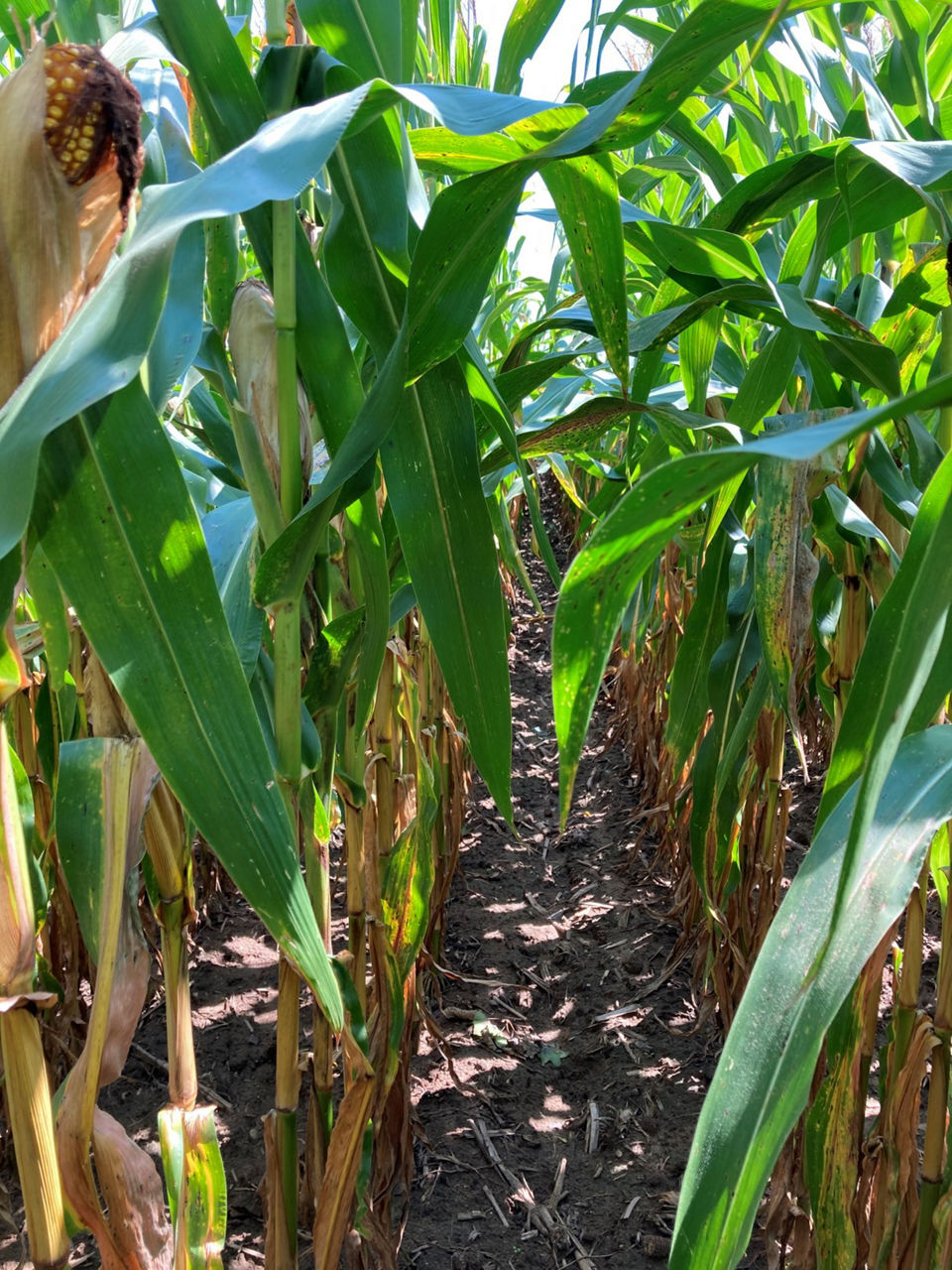



Figure 2. Untreated susceptible corn product on left, and R1 and R3 treated less susceptible corn product on right at Colon, MI (2021).


High tar spot pressure was present at Colon and moderate disease pressure at Westphalia.
A fungicide application at R1 corn growth stage at either location provided the greatest yield increase (Tables 1 and 2).
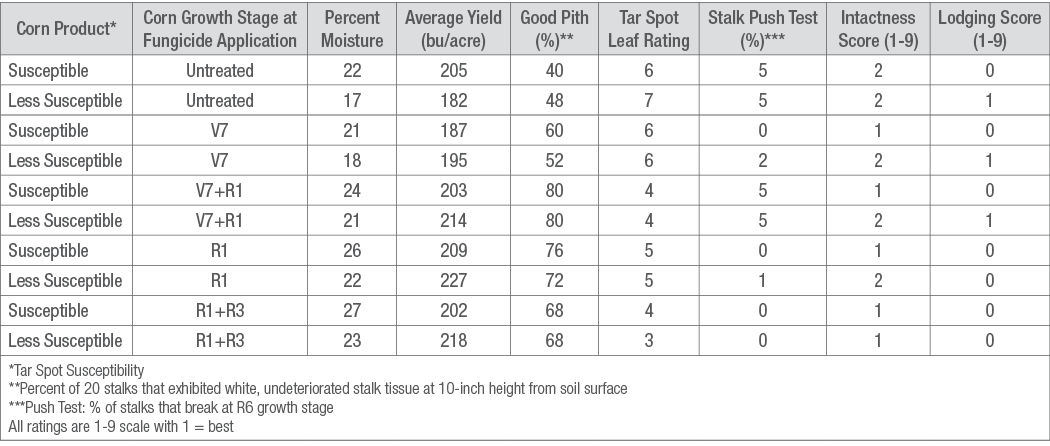
In this trial, the addition of a fungicide application at V7 corn growth stage provided improved stalk health at Colon with reduced stalk breakage in the end-of-season stalk push test (Table 1).
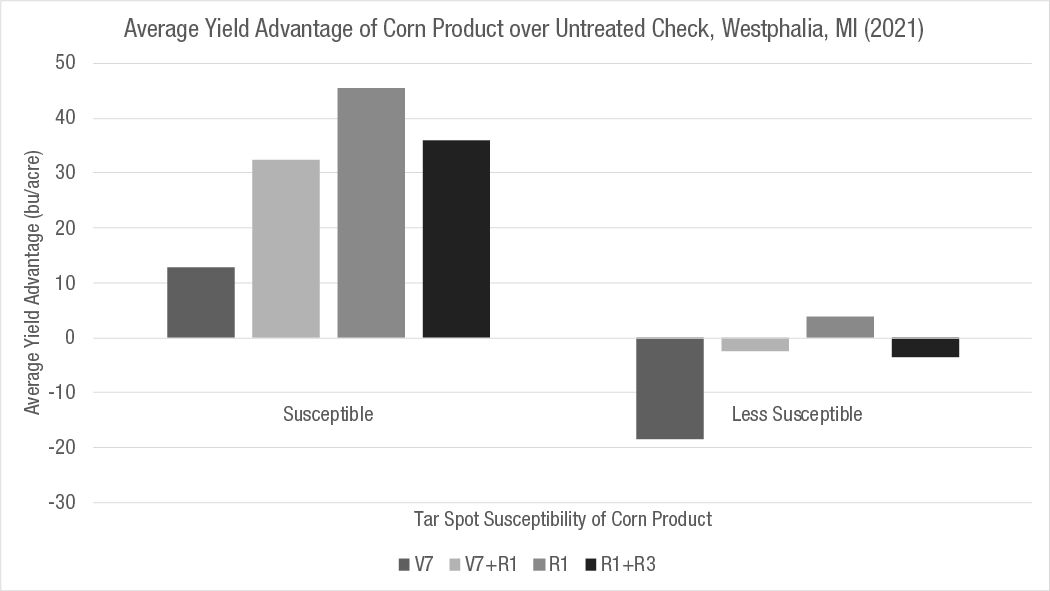
A fungicide application increased the yield of the more susceptible corn product compared to less susceptible products (Figure 1).
The addition of a second late-season application did not increase corn grain yields in Colon (Figure 1).
Table 1. End of season corn characteristics from Colon, MI (irrigated, corn on corn) tar spot fungicide timing trial.
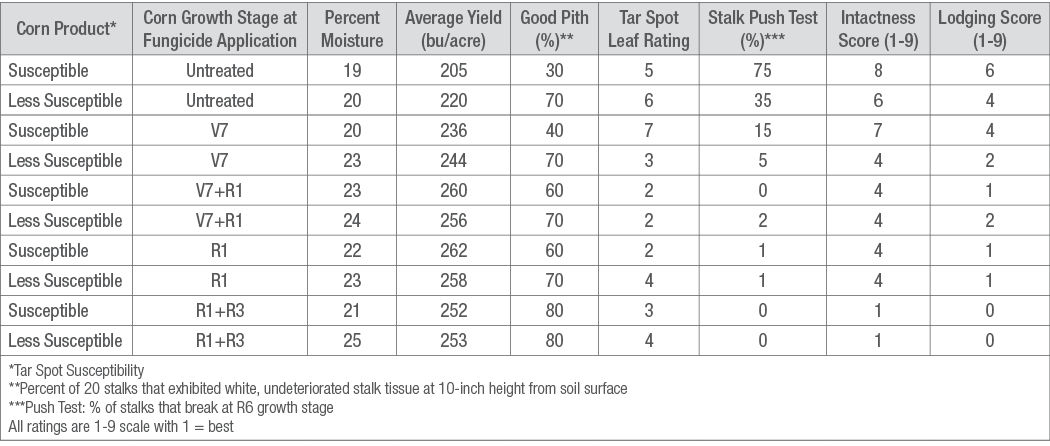
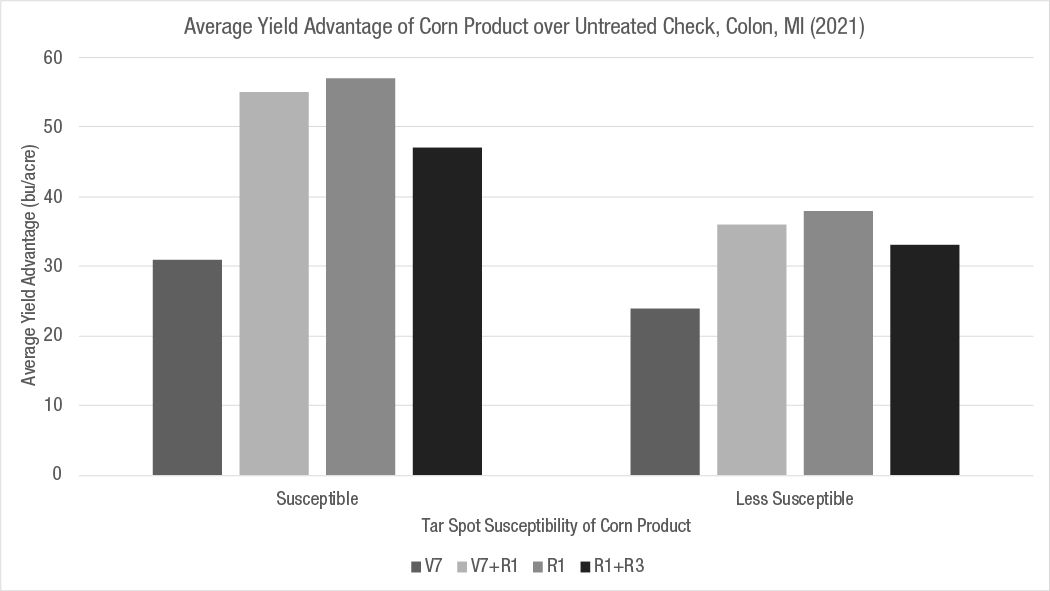
Table 2. End of season corn characteristics from Westphalia, MI (irrigated, corn on corn) tar spot fungicide timing trial.
KEY LEARNINGS
Tar spot can substantially reduce yield potential, but the use of a Delaro® Complete fungicide at R1 can help prevent loss of yield potential.
The application of a low rate of Delaro® 325 SC fungicide around V7 growth stage may help improve stalk health and late season stalk strength.
Both susceptible and less susceptible corn products benefit from an application of Delaro® Complete fungicide in fields with greater tar spot disease pressure.
5006_R1
Disclaimer
Always read and follow pesticide label directions, insect resistance management requirements (where applicable), and grain marketing and all other stewardship practices.